Sleep disorders
Types of Sleep Disorders
Insomnia:
Difficulty in falling to sleep, or staying asleep, or waking up early in the morning. It can either be acute that has a duration of a short period, or chronic that lasts long. Stress, anxiety among other medical conditions can cause it.
Sleep Apnea:
Sleep apnea is one of the deadliest condition which involves repeated breathing interruptions during sleep. It falls into two categories: one; obstructive sleep apnea, mainly caused by the blockade within the upper airway attributed to excess weight or oversized tonsils and the other known as central sleep apnea.
Central Sleep Apnea: When the brain fails to send signals to the muscles to breathe.
Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS)
An irresistible urge to move the legs. Leg symptoms are often associated with uncomfortable sensations. Symptoms often worsen at night, when they disrupt sleep.
Narcolepsy:
A chronic sleep disorder that affects the brain’s ability to regulate sleep-wake cycles. It causes excessive daytime sleepiness or sudden sleep attacks. People with this disorder may also experience cataplexy (a sudden loss of muscle tone) or disrupted nighttime sleep.
- Abnormal behaviors or experiences during sleep.
- Sleepwalking: Walking and getting out of bed while in a deep sleep.
- Night Terrors: Episodes of intense fear during sleep, usually with screaming or thrashing.
- REM Sleep Behavior Disorder: Acting out dreams during REM sleep which may result in injury.
Circadian Rhythm Disorders:
Endogenous disorders resulting from a disruption in the body’s internal clock which often controls the sleep-wake cycle. Examples include working night shifts, traveling across time zones, or maintaining irregular sleep schedules.
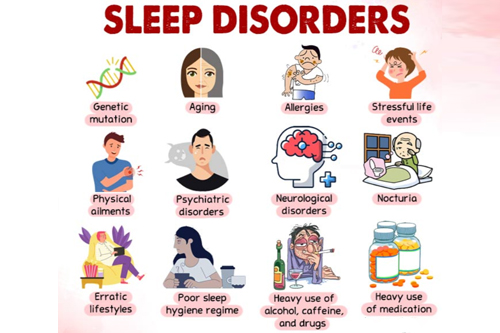
Causes and Risk Factors:
- The role of genetic predisposition in conditions like narcolepsy and sleep apnea.
- Impact of poor sleep hygiene
- Effects of irregular sleep schedules on the circadian rhythm.
- Stress, anxiety, and depression as contributing factors to insomnia and other disorders.
- The interaction between mental health and sleep.
- Chronic pain, respiratory disorders, and neurological issues that can interfere with sleep.
- Role of conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and obesity in causing sleep disturbances.
- How age affects sleep patterns and disorders (children vs. adults, older adults).
- Gender differences in sleep issues (e.g., pregnancy, menopause, and hormonal changes).
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Sleep Disorders
- Fatigue, irritability, difficulty concentrating, mood swings, and headaches.
- Importance of a thorough medical history, sleep diaries, and questionnaires.
- Medical tests and evaluations (polysomnography, actigraphy, home sleep tests).
- Discuss when sleep disturbances become a concern and when professional help should be sought.
- The role of sleep specialists and clinics in diagnosing complex sleep disorders.
Impact of Sleep Disorders on Health
- Increased risk of hypertension, heart disease, stroke, and diabetes.
- Weight gain and obesity linked to insufficient sleep.
- Correlation between poor sleep and mood disorders like depression and anxiety.
- Effects on cognitive functions like memory, concentration, and decision-making.
- How sleep disorders affect work performance, relationships, and daily functioning.Contact Us
Treatment and Management of Sleep Disorders
- Tips for improving sleep environment and habits (regular sleep schedule, bedroom environment).
- Avoiding stimulants and creating a calming pre-sleep routine.
- The role of CBT-I in treating insomnia through changing negative thought patterns around sleep.
- Evidence of effectiveness compared to medication.
- Overview of sleep medications: sedatives, benzodiazepines, and antidepressants.
- Risks and side effects of long-term use, including dependency.
- Explanation of CPAP therapy for sleep apnea patients.
Benefits, challenges, and effectiveness of CPAP machines.
- For severe cases of sleep apnea, including surgery to remove excess tissue or correct anatomical issues.
- How sleep disorders affect work performance, relationships, and daily functioning.
- Relaxation techniques (yoga, meditation, progressive muscle relaxation).
- Acupuncture, aromatherapy, and their potential benefits.Schedule your Consultation with Dr. Ritesh Nawkhare
