Prenatal diagnosis
Why Prenatal Diagnosis Matters
Prenatal diagnosis plays a critical role in modern healthcare for several reasons. First, it provides expectant parents with crucial information about their baby’s health. Early detection of conditions such as Down syndrome, spina bifida, or congenital heart defects enables parents to seek specialized care and make informed decisions about their pregnancy.
Prenatal diagnosis plays a critical role in modern healthcare for several reasons. First, it provides expectant parents with crucial information about their baby’s health. Early detection of conditions such as Down syndrome, spina bifida, or congenital heart defects enables parents to seek specialized care and make informed decisions about their pregnancy.
Types of Prenatal Diagnostic Tests
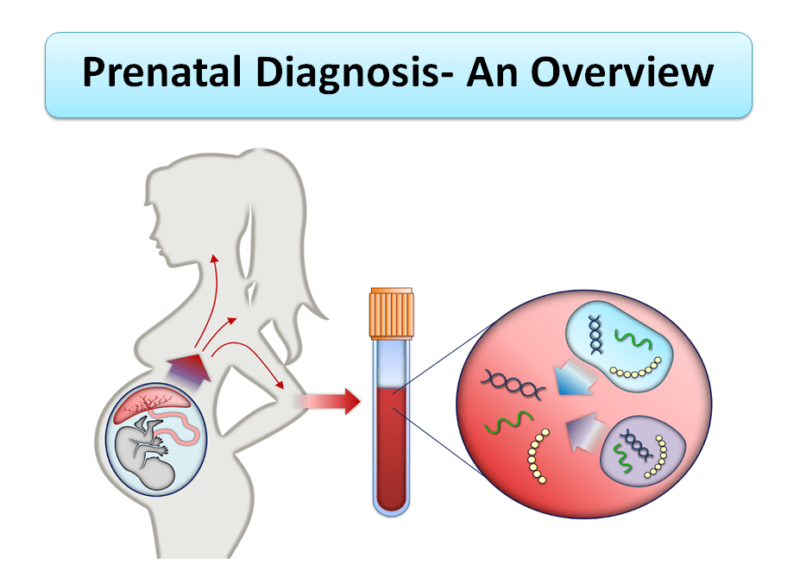
1. Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT)
Non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) is a cutting-edge screening method that analyzes cell-free fetal DNA in the mother’s blood. This test can detect chromosomal abnormalities such as Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, and Patau syndrome with high accuracy. NIPT is typically performed after the 10th week of pregnancy and poses no risk to the fetus.
Non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) is a cutting-edge screening method that analyzes cell-free fetal DNA in the mother’s blood. This test can detect chromosomal abnormalities such as Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, and Patau syndrome with high accuracy. NIPT is typically performed after the 10th week of pregnancy and poses no risk to the fetus.
2. Ultrasound Imaging
Ultrasound imaging is one of the most widely used tools in prenatal diagnosis. This non-invasive technique uses sound waves to create images of the fetus, allowing healthcare providers to assess its growth and development. Ultrasounds can detect structural abnormalities, such as cleft lip, heart defects, and neural tube defects, as well as confirm the baby’s gestational age and position.
There are different types of ultrasound scans, including standard 2D ultrasounds, 3D ultrasounds, and 4D ultrasounds. Each type offers varying levels of detail, with 3D and 4D ultrasounds providing more comprehensive views of the fetus. Ultrasounds are typically performed at different stages of pregnancy, with the first-trimester scan being particularly important for early detection of potential issues.
3. Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) is an invasive diagnostic procedure that involves collecting a small sample of placental tissue. This tissue contains genetic material from the fetus, which can be analyzed for chromosomal abnormalities and genetic disorders. CVS is usually performed between the 10th and 13th weeks of pregnancy.
One of the main advantages of CVS is its early timing, allowing parents to receive diagnostic information sooner than with other methods. However, CVS carries a small risk of miscarriage and other complications, making it essential for parents to weigh the benefits and risks before proceeding.
4. Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis is another invasive diagnostic test that involves extracting a small amount of amniotic fluid from the uterus. This fluid contains fetal cells that can be analyzed for genetic and chromosomal abnormalities. Amniocentesis is typically performed between the 15th and 20th weeks of pregnancy.
Like CVS, amniocentesis provides definitive diagnostic information but carries a small risk of complications, including miscarriage. It is often recommended for women with abnormal screening test results or those at higher risk of genetic disorders due to age or family history.
5. Maternal Serum Screening
Maternal serum screening, also known as the triple or quadruple screen, is a blood test that measures specific markers in the mother’s blood. These markers can indicate the likelihood of certain conditions, such as Down syndrome, neural tube defects, and trisomy 18. The test is usually performed between the 15th and 20th weeks of pregnancy.
While maternal serum screening is non-invasive and poses no risk to the fetus, it is not diagnostic. Abnormal results may prompt further testing, such as amniocentesis or CVS, to confirm the diagnosis.
Benefits of Prenatal Diagnosis
Prenatal diagnosis offers numerous benefits for expectant parents and healthcare providers. Below, we explore some of the key advantages.
1. Early Detection of Health Issues
One of the most significant benefits of prenatal diagnosis is the early detection of health issues. Identifying conditions such as chromosomal abnormalities, genetic disorders, and structural defects early in pregnancy allows parents to seek specialized care and make informed decisions about their pregnancy.
2. Improved Pregnancy Management
Prenatal diagnosis enables healthcare providers to develop tailored treatment plans for both mother and baby. For example, if a heart defect is detected, specialists can monitor the baby’s development closely and plan for surgery after birth. This proactive approach improves outcomes and reduces the risk of complications.
3. Emotional Preparation
Prenatal diagnosis enables healthcare providers to develop tailored treatment plans for both mother and baby. For example, if a heart defect is detected, specialists can monitor the baby’s development closely and plan for surgery after birth. This proactive approach improves outcomes and reduces the risk of complications.
4. Informed Decision-Making
Prenatal diagnosis enables healthcare providers to develop tailored treatment plans for both mother and baby. For example, if a heart defect is detected, specialists can monitor the baby’s development closely and plan for surgery after birth. This proactive approach improves outcomes and reduces the risk of complications.
Ethical Considerations in Prenatal Diagnosis
1. Informed Consent
2. Privacy and Confidentiality
3. Potential for Discrimination
4. Emotional Impact
5. Access and Equity
The Future of Prenatal Diagnosis
1. Advances in Non-Invasive Testing
2. Integration of Artificial Intelligence
3. Expanded Genetic Screening
4. Ethical and Policy Developments
5. Personalized Medicine
The future of prenatal diagnosis may also involve a shift toward personalized medicine, where diagnostic tests and treatments are tailored to the individual needs of each mother and baby. This approach has the potential to improve outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.Contact Us
Conclusion
Prenatal diagnosis is a powerful tool that offers expectant parents valuable insights into the health and development of their unborn child. By understanding the various methods, benefits, and ethical considerations, parents can make informed decisions and prepare for the journey ahead. As the field continues to evolve, ongoing advancements in technology and genetics promise to further enhance the accuracy, accessibility, and impact of prenatal diagnosis. Ultimately, the goal is to ensure the best possible outcomes for both mother and baby, empowering families to navigate the challenges and joys of pregnancy with confidence and clarity.Schedule your Consultation with Dr. Ritesh Nawkhare
