Neuromuscular disorders
Neuromuscular disorders are a group of conditions that affect the nerves controlling voluntary muscles, causing muscle weakness, degeneration, and other complications. These disorders can be genetic, autoimmune, or acquired due to infections, metabolic imbalances, or trauma. Early diagnosis and management are crucial to improving quality of life. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore different types of neuromuscular disorders, their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
What Are Neuromuscular Disorders?
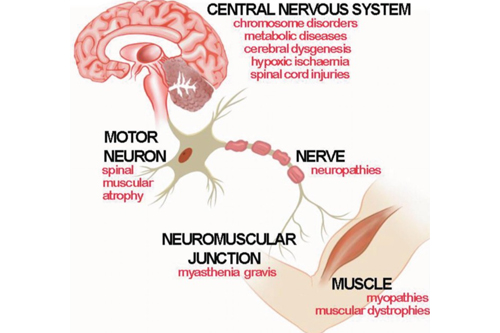
Neuromuscular disorders encompass a wide range of conditions affecting the communication between nerves and muscles. They can involve the peripheral nervous system, including the neuromuscular junction, motor neurons, and muscle fibers. These disorders often lead to progressive muscle weakness, mobility issues, and, in severe cases, respiratory or cardiac complications.
Common Types of Neuromuscular Disorders
1. Muscular Dystrophy (MD)
- Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) – Affects children, especially boys, and leads to severe muscle wasting.
- Becker Muscular Dystrophy (BMD) – Similar to DMD but with later onset and slower progression.
- Myotonic Dystrophy – Causes muscle stiffness, weakness, and systemic issues affecting the heart and endocrine system.
2. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
Also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease, ALS is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects motor neurons, leading to muscle atrophy, weakness, and eventually respiratory failure.
3. Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA)
A genetic disorder that affects the spinal cord’s motor neurons, leading to muscle weakness , atrophy. It primarily affects infants and children.
4. Myasthenia Gravis (MG)
An autoimmune neuromuscular disorder where antibodies attack the neuromuscular junction, leading to muscle fatigue and weakness, particularly in the eyes, face, and throat.
5. Peripheral Neuropathy
A condition caused by damage to peripheral nerves, leading to numbness, tingling, muscle weakness, and pain. It can be a result of diabetes, infections, or toxins.
6. Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS)
An autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks the peripheral nerves, leading to sudden weakness, tingling, and, in severe cases, paralysis.
7. Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome (LEMS)
A rare autoimmune disorder affecting the neuromuscular junction, often associated with lung cancer. It leads to muscle weakness, particularly in the limbs.
8. Mitochondrial Myopathies
Genetic disorders caused by mutations in mitochondrial DNA, leading to muscle weakness, exercise intolerance, and systemic involvement.
Causes of Neuromuscular Disorders
Neuromuscular disorders can be caused by:
- Genetic mutations – Many disorders, such as muscular dystrophy and SMA, are inherited.
- Autoimmune reactions – Disorders like MG and GBS result from the immune system mistakenly attacking neuromuscular components.
- Metabolic and mitochondrial dysfunction – Errors in metabolism or mitochondrial function can lead to muscle degeneration.
- Infections and toxins – Certain infections (e.g., viral infections) and exposure to toxins (e.g., heavy metals) can damage nerves and muscles.
- Aging and degenerative conditions – Conditions like ALS are often associated with aging and progressive nerve degeneration.
Symptoms of Neuromuscular Disorders
- Progressive muscle weakness
- Difficulty with movement and coordination
- Muscle cramps or twitching (fasciculations)
- Fatigue and muscle atrophy
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
- Numbness or tingling sensations
- Loss of reflexes
Diagnosis of Neuromuscular Disorders:
- Physical Examination: Assessment of muscle strength, reflexes, and coordination.
- Electromyography (EMG): Measures electrical activity in muscles and can detect abnormalities in nerve or muscle function.
- Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS): Tests how well electrical signals travel along nerves.
- Muscle Biopsy: A small sample of muscle tissue is examined under a microscope to look for structural abnormalities.
- Genetic Testing: Identifies specific mutations responsible for inherited neuromuscular diseases.
- Blood Tests: Used to check for abnormal levels of muscle enzymes, autoantibodies, or other markers.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Used to detect muscle or nerve damage and inflammation.
Treatment and Management of Neuromuscular Disorders
1. Medications
- Corticosteroids and immunosuppressants – Used for autoimmune disorders like MG and GBS.
- Anticholinesterase inhibitors – Improve neuromuscular transmission in MG.
- Riluzole and Edaravone – Approved treatments for ALS to slow disease progression.
- Pain relievers and anti-seizure drugs – Helps manage symptoms of neuropathy.
2. Physical and Occupational Therapy
- Strengthens muscles and improves mobility.
- Helps patients maintain independence in daily activities.
3. Assistive Devices
- Wheelchairs, braces, and mobility aids provide support.
- Non-invasive ventilation (e.g., CPAP or BiPAP) for respiratory complications.
4. Gene Therapy and Stem Cell Research
- Emerging treatments targeting genetic mutations in conditions like SMA and DMD show promise for disease modification.
5. Lifestyle Modifications
- Exercise or physical activity – Helps maintain muscle function.
- Healthy diet – Supports overall muscle or nerve health.
- Stress management – Helps prevent exacerbation of symptoms in autoimmune conditions
Prognosis and Quality of Life
The prognosis for neuromuscular disorders varies depending on the type and severity. Some conditions, like MG, can be managed effectively, while others, like ALS, progress more rapidly. Early diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation play a key role in improving quality of life.Contact Us
Conclusion
Neuromuscular disorders are a diverse group of conditions affecting muscle function and nerve communication. Advances in medical research continue to improve diagnosis and treatment, offering hope to patients with these conditions. Early intervention, rehabilitation, and emerging therapies can significantly enhance the quality of life for individuals affected by neuromuscular disorders.
If you or a loved one experience symptoms of neuromuscular disorders, consult a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and management.Schedule your Consultation with Dr. Ritesh Nawkhare
