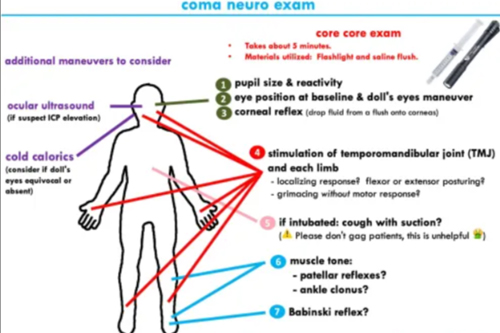
Neurological examination
A neurological examination is a detailed assessment of the nervous system performed by a healthcare provider to diagnose neurological conditions. It evaluates various functions such as motor skills, sensory response, coordination, reflexes, and mental status. A neurological exam is crucial in identifying disorders like stroke, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and neuropathies.
Importance of Neurological Examination
- Diagnosing neurological diseases and disorders
- Assessing brain function and nerve integrity
- Monitoring disease progression
- Evaluating the impact of injuries
Components of a Neurological Examination:
1. Mental Status Examination
- Orientation: Awareness of time, place, and person
- Memory: Immediate, short-term, and long-term recall
- Attention and Concentration: Ability to focus
- Language and Speech: Verbal fluency and comprehension
- Problem-Solving Skills: Logic and reasoning abilities
2. Cranial Nerve Examination
- Olfactory Nerve (CN I) – Smell detection
- Optic Nerve (CN II) – Vision and field tests
- Oculomotor (CN III), Trochlear (CN IV), Abducens (CN VI) – Eye movements and pupil response
- Trigeminal Nerve (CN V) – Facial sensation and jaw movements
- Facial Nerve (CN VII) – Facial muscle movements and expressions
- Vestibulocochlear Nerve (CN VIII) – Hearing and balance
- Glossopharyngeal (CN IX) & Vagus (CN X) Nerves – Swallowing and gag reflex
- Accessory Nerve (CN XI) – Shoulder and neck strength
- Hypoglossal Nerve (CN XII) – Tongue movement
3. Motor System Examination
- Muscle Strength: Graded from 0 (no movement) to 5 (full strength)
- Muscle Tone: Checking for rigidity or flaccidity
- Gait Analysis: Walking patterns to detect abnormalities
- Coordination Tests: Finger-to-nose test, heel-to-shin test
4. Sensory System Examination
- Pain and Temperature – Pinprick tes
- Vibration and Proprioception – Tuning fork test
- Light Touch and Discrimination – Cotton swab test
5. Reflexes Testing
- Deep Tendon Reflexes (DTRs): Knee-jerk, ankle-jerk, and biceps reflexes
- Plantar Reflex (Babinski Sign): Determines upper motor neuron lesions
- Hoffman’s Reflex: Indicates spinal cord pathology
6. Coordination and Balance Tests
- Romberg’s Test: Balance with eyes closed
- Heel-to-Toe Walking: Coordination check
- Rapid Alternating Movements: Tests fine motor control
7. Autonomic Nervous System Examination
- Heart Rate and Blood Pressure Response: Indicates autonomic dysfunction
- Sweat Tests: Evaluates nerve-related sweating issues
- Pupillary Response: Reaction to light and accommodation
Special Tests in Neurological Examination
- Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS): Evaluates consciousness in trauma cases
- Electromyography (EMG): Analyzes muscle activity
- Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS): Measures nerve function
- Lumbar Puncture (Spinal Tap): Examines cerebrospinal fluid
- Neuroimaging (MRI, CT Scan): Provides detailed brain and spinal cord images
Common Neurological Disorders Diagnosed
A neurological exam helps detect disorders such as:
- Stroke: Sudden loss of brain function due to blood supply issues
- Parkinson’s Disease: A movement disorder affecting coordination
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS): Autoimmune disease damaging nerve coverings
- Neuropathy: Nerve damage causing pain, numbness, or weakness
- Epilepsy: Recurrent seizures due to abnormal electrical activity
When Should You Get a Neurological Examination?
- Persistent headaches or dizziness
- Weakness or numbness in limbs
- Loss of coordination or balance
- Difficulty speaking or memory issues
- Unexplained seizures or tremorsContact Us
Conclusion
A neurological examination is an essential diagnostic tool for detecting and managing neurological disorders. It involves a series of systematic tests that evaluate brain function, motor skills, sensory response, and reflexes. Early detection through a neurological exam can lead to timely interventions and better health outcomes.Schedule your Consultation with Dr. Ritesh Nawkhare
