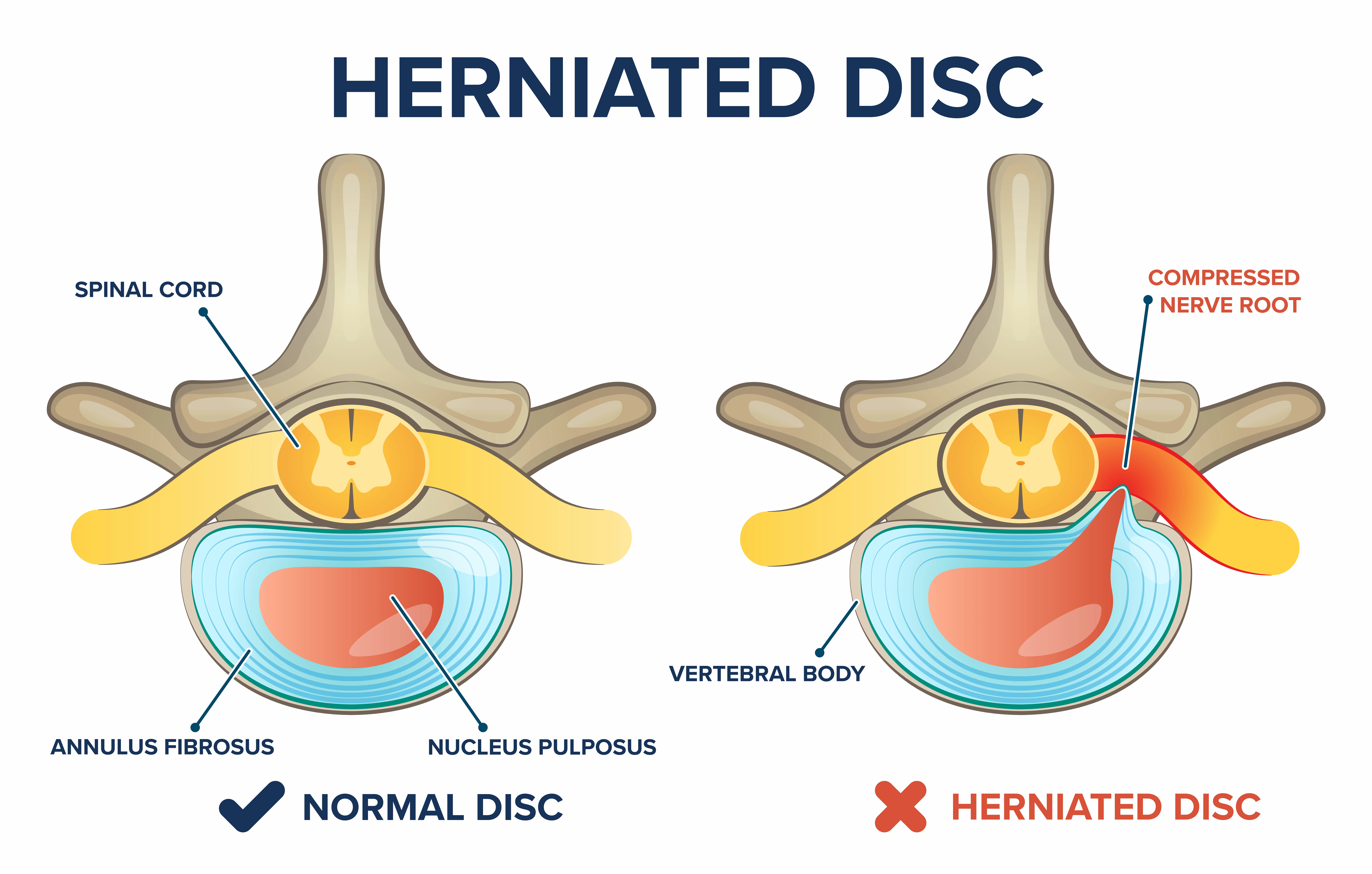
Herniated disc
A herniated disc in nagpur is basically an impairment to one of the spongy pads, known as the disks, between the bones that stack to form of the spine. These bones are known as vertebrae.
A spinal disk contains a soft, jelly-like center called a nucleus. The nucleus is a surrounded by a tougher, more rubbery outer layer, known as the annulus. A herniated disk happens when some of the nucleus pushes out through a tear in the annulus. Sometimes this is called a slipped disk or a ruptured disk.
Causes
- Degeneration: Over time, spinal discs can lose their water content and become less flexible, making them prone to tears.
- Injury or Trauma: Sudden movements, falls, or lifting heavy objects can cause a disc to rupture.
- Repetitive Strain: Repetitive activities that strain the spine, such as bending, lifting, or twisting, can increase the risk.
- Genetics: Some people may have a genetic predisposition to the herniated discs.
Symptoms
The symptoms of a herniated disc can vary depending on the location of the herniation and whether it compresses a nerve:
Lower Back (Lumbar Spine):
– Sciatica: Sharp, shooting pain that radiates from the lower back down through the buttocks or legs.
– Leg pain: Pain, tingling, or numbness that usually affects one side of the body.
– Weakness: Difficulty lifting or holding items, or walking due to leg weakness.
Neck (Cervical Spine):
– Neck pain: Sharp or radiating pain in the neck, shoulders, or arms.
– Arm pain: Tingling, numbness, or weakness in the arms and fingers.
Thoracic Spine (Middle Back):
– Less common but may cause pain radiating to the chest or abdomen.
Diagnosis
- Physical Exam: Evaluation of reflexes, muscle strength, and pain response to determine nerve involvement.
- Imaging Tests:
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): The most commonly used test to visualize herniated discs and nerve compression.
- CT Scan: Sometimes used to get detailed images of the spine.
- X-rays: Used to rule out other causes of back pain, such as fractures.
- Myelogram: A special type of X-ray that uses dye to detect pressure on the spinal cord.
Treatment Options
1. Conservative Treatments
- Rest and Activity Modification: Avoid activities can worsen symptoms.
- Pain Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help reduce pain.
- Physical Therapy: Strengthening exercises, stretching, and posture correction can relieve pressure on the spine.
- Hot and Cold Therapy: Alternating between heat and ice packs can help reduce inflammation and pain.
- Epidural Steroid Injections: In severe cases, doctors may recommend injections to reduce inflammation around the nerve.
2. Surgical Treatments
- Discectomy: Removal of herniated portion the disc.
- Laminectomy: Removal of portion the vertebra to relieve pressure.
- Spinal Fusion: Fusing two vertebrae together to stabilize the spine.
Preventing a Herniated Disc
- Maintain Proper Posture
Always sit and stand with proper spinal alignment. Use ergonomic chairs and avoid slouching. - Exercise Regularly
Strengthening the core muscles provides better spinal support and reduces strain on the discs. - Lift Objects Correctly
Always bend at the knees and keep the object close to your body when lifting. - Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess weight puts stress on the spine. A balanced diet and regular exercise can help maintain an optimal weight. - Stay Hydrated
Proper hydration keeps the spinal discs healthy and prevents degeneration. - Quit Smoking
Smoking reduces blood supply to spinal discs, leading to degeneration and an increased risk of herniation.Contact Us
Conclusion
A herniated disc can be a painful and debilitating condition, but with proper care, treatment, and lifestyle adjustments, most people can manage their symptoms and prevent further complications. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps toward spinal health. If you experience persistent back pain, it is always advisable to seek medical attention for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.Schedule your Consultation with Dr. Ritesh Nawkhare
