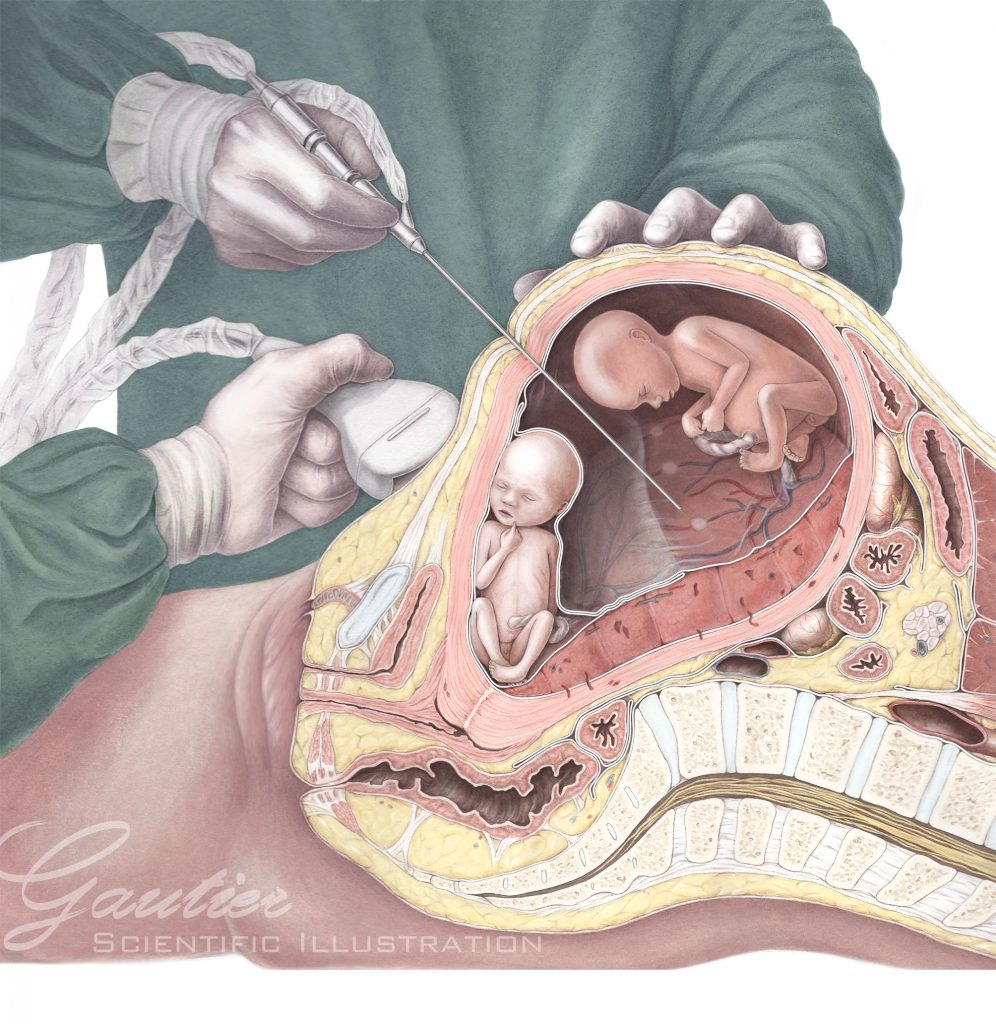
Fetal surgery
Fetal surgery represents a groundbreaking advancement in modern medicine, offering hope and life-saving interventions for unborn babies with severe congenital conditions. This detailed guide explores the intricacies of fetal surgery, its types, benefits, risks, and the transformative impact it has on maternal and fetal health. By understanding this innovative field, expectant parents and healthcare providers can make informed decisions about prenatal care.
What Is a Fetal surgery?
Fetal surgery refers to surgical procedures performed on a fetus while still in the womb. These interventions aim to correct life-threatening congenital anomalies or conditions that could severely impact the baby’s quality of life after birth. Unlike traditional postnatal surgeries, fetal surgery requires highly specialized techniques and a multidisciplinary team of experts, including maternal-fetal medicine specialists, pediatric surgeons, neonatologists, and anesthesiologists.
The primary goal of fetal surgery is to address abnormalities early, often before they cause irreversible damage. This proactive approach can significantly improve outcomes for both the baby and the mother.
Types of Fetal Surgery
Fetal surgery encompasses a range of procedures, each tailored to address specific conditions. Below are the main types of fetal surgeries.
1. Open Fetal Surgery
- Spina Bifida: A neural tube defect where the spine and spinal cord do not form properly.
- Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia (CDH): A condition where the diaphragm does not fully develop, allowing abdominal organs to move into the chest cavity.
- Twin-to-Twin Transfusion Syndrome (TTTS): A complication in identical twins where blood flow becomes imbalanced between the babies.
2. Minimally Invasive Fetal Surgery
Minimally invasive techniques, such as fetoscopy, use small incisions and specialized instruments to perform surgery. These procedures are less risky and often preferred when possible. Common conditions treated with minimally invasive surgery include:
- Twin Reversed Arterial Perfusion (TRAP) Sequence: A rare condition in twins where one baby lacks a functioning heart.
- Lower Urinary Tract Obstruction (LUTO): A blockage in the fetal urinary tract that can lead to kidney damage.
- Amniotic Band Syndrome: A condition where fibrous bands in the womb restrict blood flow to fetal limbs.
3. Ex-Utero Intrapartum Treatment (EXIT)
The EXIT procedure is performed during delivery, typically via cesarean section. It allows surgeons to address life-threatening conditions while the baby remains connected to the placenta for oxygen. Common uses include:
- Removing lung masses or tumors.
- Managing airway obstructions.
- Treating congenital heart defects.
4. Fetal Shunt Placement
The EXIT procedure is performed during delivery, typically via cesarean section. It allows surgeons to address life-threatening conditions while the baby remains connected to the placenta for oxygen. Common uses include:
- Hydrothorax: Fluid buildup in the chest cavity.
- Hydrocephalus: Excess cerebrospinal fluid in the brain.
Conditions Treated with Fetal Surgery
Benefits of Fetal Surgery
- Improved Survival Rates: Many conditions treated with fetal surgery have significantly higher survival rates compared to postnatal treatment.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Early intervention can reduce long-term disabilities and improve developmental outcomes.
- Reduced Complications: Addressing issues before birth can prevent secondary complications, such as organ damage or respiratory failure.
- Emotional Relief for Parents: Knowing that their baby has received the best possible care can provide immense emotional relief to expectant parents.
Risks and Challenges of Fetal Surgery
- Premature Labor: Surgery can trigger early labor, leading to preterm birth.
- Infection: Any surgical procedure carries risk of infection.
- Maternal Complications: The mother may experience bleeding, blood clots, or other surgical complications.
- Fetal Risks: The fetus may experience distress or injury during the procedure.
The Fetal Surgery Process
1. Diagnosis and Evaluation
The EXIT procedure is performed during delivery, typically via cesarean section. It allows surgeons to address life-threatening conditions while the baby remains connected to the placenta for oxygen. Common uses include:
2. Preoperative Planning
Once surgery is deemed necessary, the team develops a detailed plan, including the type of surgery, timing, and potential risks. Parents receive comprehensive counseling to understand the procedure and its implications
3. The Surgical Procedure
The surgery is performed in a specialized fetal treatment center with state-of-the-art equipment. The mother receives anesthesia to ensure her comfort and safety, while the fetus is carefully monitored throughout the procedure.
4. Postoperative Care
After surgery, both the mother and fetus require close monitoring. The mother may need to remain on bed rest or take medications to prevent preterm labor. Follow-up scans and tests ensure the fetus is healing properly.
5. Delivery and Beyond
In many cases, delivery is scheduled via cesarean section to minimize risks. After birth, the baby may require additional treatments or surgeries, depending on the condition.
The Role of Maternal-Fetal Medicine Specialists
Maternal-fetal medicine (MFM) specialists play a critical role in fetal surgery. These experts are trained to manage high-risk pregnancies and work closely with surgeons, neonatologists, and other specialists to provide comprehensive care. Their responsibilities include:
- Diagnosing fetal conditions.
- Counseling parents about treatment options.
- Coordinating surgical interventions.
- Monitoring the mother and fetus throughout the pregnancy.
Advances in Fetal Surgery
Maternal-fetal medicine (MFM) specialists play a critical role in fetal surgery. These experts are trained to manage high-risk pregnancies and work closely with surgeons, neonatologists, and other specialists to provide comprehensive care. Their responsibilities include:
- Robotic-Assisted Surgery: Enhances precision in minimally invasive procedures.
- 3D Printing: Allows surgeons to create detailed models of fetal anatomy for preoperative planning.
- Stem Cell Therapy: Holds promise for repairing damaged tissues in the womb.
Choosing a Fetal Surgery Center
Selecting the right fetal surgery center is crucial for ensuring the best possible outcomes. Factors to consider include:
- The center’s experience and success rates.
- The availability of a multidisciplinary team.
- Access to advanced diagnostic and surgical technologies.
- Emotional and logistical support for families.
Conclusion
Fetal surgery is a remarkable achievement in modern medicine, offering hope and healing for unborn babies with life-threatening conditions. While it carries risks, the potential benefits—improved survival rates, enhanced quality of life, and reduced complications—make it a valuable option for many families. By working with a skilled and experienced team, parents can give their baby the best possible start in life.Contact Us
If you are considering fetal surgery, consult with a maternal-fetal medicine specialist to explore your options and make an informed decision. With the right care and support, you can navigate this complex journey with confidence and hope.Schedule your Consultation with Dr. Ritesh Nawkhare
