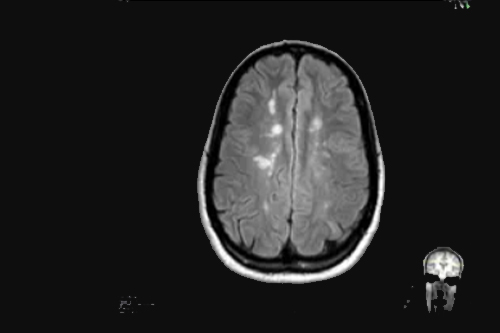
Autoimmune neurological disorders
Autoimmune neurological disorders are a group of conditions in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the nervous system, leading to serious health complications. With the rising prevalence of such disorders, access to specialized healthcare is crucial. In Nagpur, a growing medical hub, residents have access to expert neurologists, advanced diagnostic facilities, and cutting-edge treatment options. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options available for autoimmune neurological disorders in Nagpur.
Autoimmune neurological disorders occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy nerve cells, leading to inflammation, damage, and impaired neurological function. These disorders can affect the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves, leading to a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to severe disability.
Neuromyelitis Optica
Neuromyelitis Optica, also known as Devic’s disease, is one of the grave autoimmune diseases mainly affecting the optic nerves and the spinal cord, often accompanied by widespread inflammation and tissue damage, usually brought about by specific antibodies to the water channels in the central nervous system. If not treated early and aggressively, NMO can lead to serious disability. It affects Africans and Asians more frequently and sometimes is misdiagnosed as multiple sclerosis; it then undergoes inappropriate, even dangerous treatment. Read more on Neuromyelitis Optica
MRI image of a patient with NMO: The long tract of the inflammation along the spinal cord.
Autoimmune Brain Disease
Autoimmune brain disorders occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks and damages the tissues found in the brain or spinal cord, thus causing inflammation that affects normal functioning, often leading to a variety of neurological or psychiatric symptoms.
The children with this condition can experience poor school performance, seizures, abnormal movement disorders, eye problems, weakness in limbs, deterioration of languages, and sleep disorders. So, They may also have psychosis, hallucination, as well as the symptoms like paranoid, obsessive or errant behavior.
At times, determination of which subtype of autoimmune brain disease is diagnosed is a key early response to treatment. Among them, there are:
- Autoimmune encephalitis
- Autoimmune-related epilepsy
- Central nervous system (CNS) vasculitis
- Hashimoto’s encephalopathy also known as steroid-responsive encephalopathy
- Neuromyelitis optica
- Optic neuritis
- Neurosarcoidosis
- Neuro-Behcet’s disease
- Cerebral lupus
Above all, we are committed to provide integral treatment to these somewhat rare and challenging conditions. Thus, Our highly experienced staff ensures that there are the right treatments which can manage or minimize any number of symptoms associated with these disorders.
Common Autoimmune Neurological Disorders:
1. Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Definition: MS is a chronic autoimmune disease, whereby the immune system attacks the protective covering of nerve fibers called myelin in the CNS, leading to improper communication between the brain and the rest of the body.
Symptoms: Fatigue, muscle weakness, difficulty walking, eye problems, tingling or numbness, cognitive disturbances, and loss of balance.
Treatment: Disease-modifying treatments (DMTs) such as interferons, glatiramer acetate, and monoclonal antibodies (such as ocrelizumab) aim at reducing exacerbation rates and slowing the disease progression. Corticosteroids are given at the time of an acute exacerbation.
2. Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS)
Definition: GBS is an autoimmune condition in which the immune system attacks the peripheral nerves. It often results after a preceding infection, usually a respiratory or gastrointestinal one.
Symptoms: It begins from weakness and paresthesia, originally localized to the legs, but rapidly spread to other parts of the body, the arms included. It can cause even paralysis in very severe attacks.
Treatment: Should be treated with intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIG) or plasma exchange, also called plasmapheresis, which decreases the immune attack against nerves. The supportive care is usually provided for several weeks up to months while following recovery.
3. Myasthenia Gravis (MG): Description
MG is an immune-mediated disease at the neuromuscular junction, where nerves interact with muscles. The immune system is turned on and produces antibodies that block or destroy acetylcholine receptors, resulting in muscle weakness.
Symptoms: Muscle weakness that worsens with activity and improves at rest. Involved are those of the eyes (ptosis, diplopia), face, throat (dysphagia, dysarthric speech), and limbs.
Treatment: AChE inhibitors, such as pyridostigmine; immunosuppressors, like prednisone or azathioprine; and, in some individuals, thymectomy.
4. Neuromyelitis Optica (NMO) formerly known as Devic's disease
Definition: NMO represents an autoimmune disease where inflammation of the optic nerves and spinal cord result in damage to the tissues. It was formerly considered a form of MS but is now considered a distinct disease.
Symptoms: Sudden loss of vision, severe pain in the eyes, weakness or paralysis of limbs. The bladder and the bowel are also affected.
Treatment: Acute attacks are treated with corticosteroids and plasma exchange. Long-term treatment may include immunosuppressive therapies like rituximab or mycophenolate mofetil to prevent relapses.
5. Autoimmune Encephalitis
Description: Autoimmune syndrome, in which the immunity system attacks the brain, thus developing an inflammation caused by the antibodies use against the receptors like NMDA or any other proteins within the brain.
Symptoms: Confusion, memory loss, seizures, hallucinations, behavioral/mood changes are just a few of them. Due to the fact that this condition can develop so quickly it carries a very serious threat if not addressed on time.
Treatment: Immunosuppressive therapies, such as IVIG, plasma exchange, corticosteroids, rituximab or cyclophosphamide in some cases.
6. Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy (CIDP)
CIDP: It’s an autoimmune disease causing chronic inflammation and demyelination of the peripheral nerves, which persist beyond 8 weeks.
Symptoms: Muscle weakness, weakness starting from the bottom of the body moving upwards, impairment of sensory perception, and fatigue and heaviness in the limbs. Symptoms can vary considerably, mostly long-term but many patients experience relapsing courses.
Treatment: includes intravenous immunoglobulin, plasma exchange, corticosteroids, and immunosuppressive drugs such as azathioprine or rituximab.
7. Hashimoto's Encephalopathy
Description: A rare autoimmune condition associated with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, in which the immune system attacks the thyroid gland and sometimes affects the brain.
Symptoms : Confusion, seizures, memory problems, headaches, and psychiatric symptoms such as mood swings or hallucinations .
Treatment: High-dose corticosteroids usually employed with good response in most patients.
8. Stiff Person Syndrome (SPS)
Description: A very rare autoimmune disease characterized by stiff muscle spasms as a result of abnormal immune activity against the CNS, with a prominent action on the neurons producing GABA.
Symptoms: Chronic stiffness in the trunk and limbs, causing disabilities in carrying out motions and exaggerated sensitivity to stimuli such as noise or light touch, which can lead to spasms.
Treatment : It involves benzodiazepines, baclofen, and immunotherapies including IVIG and rituximab.
9. Paraneoplastic Neurological Syndromes (PNS)
Description: These are rare neurological disorders caused by an abnormal immune response to cancer. During this time, often before a specific diagnosis of cancer, the immune system mistakenly attacks part of the nervous system .
Symptoms: Depend on what aspect of the nervous system is affected. Symptoms can range from ataxia and sensory loss to weakness and even cognitive dysfunction .
Treatment: Treatment involves the management of the underlying cancer and immunosuppressive therapies that curb the immune response.
Causes of Autoimmune Neurological Disorders:
The exact cause of autoimmune neurological disorders is not fully understood, but it involves a combination of genetic, environmental, and immunological factors. Some potential triggers include:
- Infections: Viral or bacterial infections can sometimes trigger an autoimmune response.
- Genetic predisposition: Certain genetic factors may make individuals more susceptible to autoimmune diseases.
- Molecular mimicry: Infections or other immune challenges may cause the immune system to mistakenly attack normal tissues because they resemble foreign invaders.
- Environmental factors: Factors like toxins or certain medications may also contribute to autoimmune reactions.
Symptoms of Autoimmune Neurological Disorders
- Muscle weakness or paralysis
- Tingling, numbness, or burning sensations
- Vision disturbances, including blurred or double vision
- Difficulty swallowing or speaking
- Chronic fatigue and exhaustion
- Memory problems or cognitive decline
- Seizures or loss of consciousness
- Loss of coordination and balance
Diagnosis of Autoimmune Neurological Disorders in Nagpur
- Neurological Examination: A neurologist assesses reflexes, muscle strength, coordination, and sensory function to identify abnormalities.
- Blood Tests: These tests detect specific antibodies associated with autoimmune disorders, helping in diagnosis.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI scans provide detailed images of the brain and spinal cord to detect inflammation, lesions, or damage.
- Electromyography (EMG) and Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS): These tests measure electrical activity in muscles and nerves, helping diagnose disorders like myasthenia gravis and CIDP.
- Lumbar Puncture (Spinal Tap): A sample of cerebrospinal fluid is analyzed for signs of inflammation or infection.
Why Choose Nagpur for Autoimmune Neurological Treatment?
- Availability of highly skilled neurologists and specialists.
- State-of-the-art diagnostic and treatment facilities.
- Cost-effective healthcare compared to metro cities.
- Personalized patient care and rehabilitation services.
Preventing Autoimmune Neurological Disorders
While not all autoimmune diseases can be prevented, adopting a healthy lifestyle can reduce the risk:
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamins.
- Regular Exercise: Helps to improve circulation and reduces inflammation.
- Manage Stress: Meditation, yoga, and relaxation techniques lower stress levels.
- Avoid Smoking and Alcohol: These can trigger or worsen autoimmune responses.Contact Us
Conclusion
Autoimmune neurological disorders can be life-altering, but with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, many patients lead fulfilling lives. In Nagpur, access to specialized neurologists, advanced diagnostics, and comprehensive treatment options make it a prime location for managing these conditions. If you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms, consult a neurologist in Nagpur immediately to receive expert care and improve quality of life.Schedule your Consultation with Dr. Ritesh Nawkhare
